Thiol–ene synthesis and characterization of lithium bis(malonato)borate single-ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes†
Abstract
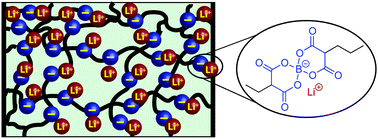
The development of high capacity anodes and high voltage cathodes for advanced lithium-ion batteries motivates the search for new polymer electrolytes that exhibit superior electrochemical stabilities and high ionic conductivities. We report a convenient, three-step synthesis of lithium bis(non-8-enyl-malonato)borate (LiBNMB) as a α,ω-diene monomer, which undergoes thermally initiated thiol–ene crosslinking polymerizations in propylene carbonate to yield gel polymer electrolytes with high lithium ion concentrations (∼0.9 M). By conducting these crosslinking polymerizations using mixtures of di- and tri-thiols and LiBNMB with [thiol] : [ene] = 1 : 1, we synthesized a series of gel networks with dynamic elastic moduli ranging from G′ = 40–79 kPa that increase monotonically with trifunctional crosslinker content. While ionic conductivities for these polymer gels measured by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at 22 °C are σ = 0.82–2.5 × 10−6 S cm−1, we show that the conductivity of propylene carbonate-solvated lithium ions though the bulk of these gel electrolytes is 8.5 × 10−5 S cm−1 independent of crosslinker density. However, the conductivities of the gel interfaces depend sensitively on crosslinker content, suggesting the importance of segmental rearrangement dynamics at the electrode interface in limiting the rate of ion motion. Thus, the design of highly conductive polymer electrolytes for advanced batteries demands careful design of both the internal and interfacial properties of these new materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...