Swelling-induced structural changes and microparticle uptake of gelatin gels probed by NMR and CLSM†
Abstract
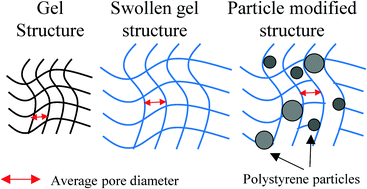
Gelatin gels are increasingly involved in many industrial applications due to several advantages including cost efficiency and biocompatibility. Generally, their production requires the use of aqueous solvents, which cause significant swelling, due to the ability of solvent molecules to penetrate through the gel microstructure and increase its volume. Since swelling mechanisms and their effect on the gel structure are not fully understood, further investigations are required. In this work, we combine macroscopic measurements of the swelling ratio (SR) with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) to investigate changes in the gelatin structure as a function of both polymer concentration and swelling time. SR values increase as a function of time until a maximum is reached and then show a slight drop for all the gelatin concentrations after 24 h swelling time, probably due to a network relaxation process. NMR allows determination of mass transport and molecular dynamics of water inside the gelatin pores, while CLSM is used to visualize the penetration of tracers (polystyrene microbeads) with a diameter much larger than the gel pores. Structural parameters, such as average pore size and tortuosity, are estimated. In particular, the pore size decreases for higher polymer concentration and increases during swelling, until reaching a maximum, and then dropping at longer times. The penetration of tracers provides evidence of the heterogeneity of the gel structure and shows that single microcarriers can be loaded in gelatin gels upon swelling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...