Structural behaviour of sodium hyaluronate in concentrated oppositely charged surfactant solutions†
Abstract
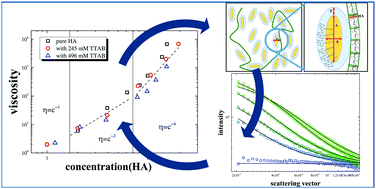
This work discusses the polyelectrolyte sodium hyaluronate (HA) and its polyelectrolyte/surfactant complexes (PESCs) with tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide (TTAB) in the semi-dilute regime of HA and at high concentrations of TTAB. The structure and flow properties in the surfactant excess region were studied by light scattering and small angle neutron scattering (SANS) as well as by rheology. The unique behaviour of HA to maintain its high viscosity was observed even at very high TTAB concentrations of 496 mM and this effect was systematically studied in the concentration range from 1 to 25 mM HA. From the data, it could be concluded that: (1) extended rod-like structures of the PESCs prevent molecular dissolution of HA by TTAB. (2) HA and TTAB micelles interact rather weakly as seen by a low fraction of bound micelles. (3) At very high TTAB concentrations a decompaction of PESCs (fractal dimension Df going from 2.0 to 1.2) occurs with increasing HA concentration but (4) both the entanglement of HA and the structure of the micelles are not affected.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...