Analytical form of the autocorrelation function for the fluorescence correlation spectroscopy†
Abstract
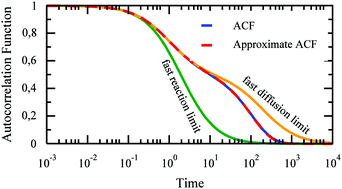
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) can provide information about diffusion coefficients and rate constants of chemical reactions in small systems of interacting molecules. However, the interpretation of FCS experiments depends crucially on the model of the autocorrelation function for the fluorescence intensity fluctuations. In this theoretical work, we consider a system of fluorescent molecules that diffuse and interact with massive particles, e.g. surfactant micelles. Using the general formalism of FCS, we derive a new analytical approximation of the autocorrelation function for systems in which both diffusion and a binary reaction occur. This approximation provides a smooth interpolation between the limit of fast reaction (much faster than diffusion), and the opposite limit of slow reaction. Our studies of noncovalent interactions of micelles with dyes by FCS provided an experimental case to which the approximate autocorrelation function was successfully applied [X. Zhang, A. Poniewierski, A. Jelińska, A. Zagożdżon, A. Wisniewska, S. Hou and R. Hołyst, Soft Matter, 2016, 12, 8186–8194].


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...