Colloidal molecules assembled from binary spheres under an AC electric field
Abstract
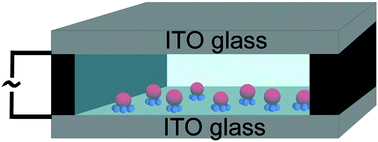
Colloidal particles are envisioned as analogues of atoms and molecules, however they often lack the complexities present in their counterparts. In this work, we report the assembly of colloidal molecules from a binary mixture of polystyrene spheres (1, 1.6, 2, and 4 μm) under an alternating current electric field. The rich family of assembled oligomers typically consists of a large sphere that is closely surrounded by a number of smaller petal particles, driven by the dipolar attraction between large and small particles. In deionized water, the number of satellite particles, i.e., the coordination number increases with the increasing size ratio of the constituent particles. For a given size ratio, the coordination number decreases with the increasing frequency of the applied field. These trends have also been correctly captured by computing the electric energy of different oligomers based on induced dipolar and double-layer interactions. By suspending the particles in polyvinylpyrrolidone aqueous solution, we can further tune the bond length of the oligomers independent of their coordination numbers. The addition of polyvinylpyrrolidone also allows us to lock the assembled colloidal molecules so that they remain intact after the electric field is turned off. Our method provides a robust way to produce a family of colloidal molecules with well-defined geometry and high yield.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...