Oxygen vacancies on TiO2 promoted the activity and stability of supported Pd nanoparticles for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
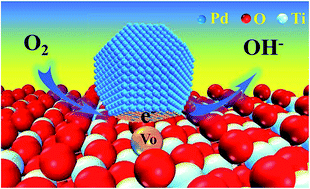
The key bottleneck of applying Pd catalysts in fuel cells is their low activity and poor stability during the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) although less precious Pd is still a promising alternative to Pt. Hence, new strategies to improve the performance of Pd in the ORR need to be developed. In this study, supported Pd (3.6 nm in average) catalysts on TiO2 with and without oxygen vacancies (VO) have been prepared via facile pyrolysis. Compared with commercial Pt/C (20 wt%) and Pd/TiO2 catalysts, Pd/TiO2-VO (10 wt%) demonstrated superior oxygen reduction activity, better durability, and higher methanol tolerance capability in alkaline solution. By means of experimental characterizations (ESR and XPS) and density functional theory (DFT) calculations, electron transfer from TiO2-VO to Pd nanoparticles (NPs) led to an electron-rich Pd surface and strong metal–support interactions (SMSIs). The electron-rich Pd NPs enhanced the adsorptions of key intermediates, lowered the Gibbs free energy of the ORR, and improved the ORR activity. SMSIs between Pd NPs and TiO2-VO endowed the catalyst with excellent stability and immunity to methanol poisoning. Therefore, the electron transfer from TiO2-VO to Pd NPs plays a crucial role in promoting the ORR performance of Pd-based electrocatalysts, which may be a new strategy to design high-performance ORR catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...