Chicoric acid supplementation ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by oxidative stress via promotion of antioxidant defense system
Abstract
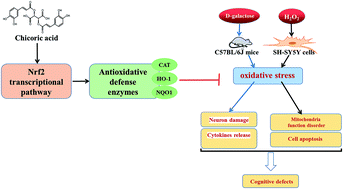
Chicoric acid, a nutritional component found in the Mediterranean vegetable chicory, possesses multiple biological properties including antioxidant activities, anti-obesity effects, anti-HIV, and others. However, there have been very few studies of its effects to counter oxidative stress-induced cognitive loss. To address this, the goal of this study was to investigate the effects of chicoric acid on oxidative stress induced both in the brain of C57BL/6J mice and in SH-SY5Y cells. The C57BL/6J mice induced by D-galactose (D-gal; 300 mg kg−1 d−1 body weight, intraperitoneal injection for 2 months) and SH-SY5Y cells induced by H2O2 were used to evaluate protective effects of chicoric acid (100 mg kg−1 d−1 body weight in drinking water for 8 weeks). The learning and memory abilities were assessed using the Y-maze and Morris maze tests. Chicoric acid attenuated neuron damage in D-gal-treated mice as revealed through histological examination in the hippocampus region of the mouse brain. The levels of inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, as well as malondialdehyde levels, were markedly reduced after chicoric acid treatment. In contrast, the activity of CAT and the level of GSH were significantly elevated in serum by chicoric acid. The results also revealed that chicoric acid treatment noticeably activated the Nrf2 antioxidative defense system by up-regulation of downstream antioxidant enzyme expression both in the animal and the cell models. The chicoric acid regulation mechanism may be associated with balancing cellular redox status, reversing mitochondrial dysfunction, decreasing inflammation, and neuron apoptosis caused by oxidative stress. These results suggested that chicoric acid supplementation ameliorated cognitive impairment induced by D-gal and SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis induced by H2O2 via promotion of the Keap1/Nrf2 signal pathway and its downstream antioxidant enzymes, indicating that chicoric acid has great potential for use as part of a nutritional preventive strategy to counter oxidative stress-related cognitive impairment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...