The influence of acceptor nucleophilicity on the glycosylation reaction mechanism†
Abstract
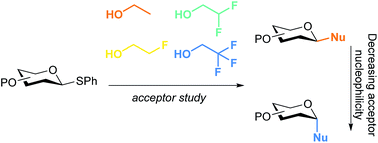
A set of model nucleophiles of gradually changing nucleophilicity is used to probe the glycosylation reaction mechanism. Glycosylations of ethanol-based acceptors, bearing varying amounts of fluorine atoms, report on the dependency of the stereochemistry in condensation reactions on the nucleophilicity of the acceptor. Three different glycosylation systems were scrutinized, that differ in the reaction mechanism, that – putatively – prevails during the coupling reaction. It is revealed that the stereoselectivity in glycosylations of benzylidene protected glucose donors are very susceptible to acceptor nucleophilicity whereas condensations of benzylidene mannose and mannuronic acid donors represent more robust glycosylation systems in terms of diastereoselectivity. The change in stereoselectivity with decreasing acceptor nucleophilicity is related to a change in reaction mechanism shifting from the SN2 side to the SN1 side of the reactivity spectrum. Carbohydrate acceptors are examined and the reactivity–selectivity profile of these nucleophiles mirrored those of the model acceptors studied. The set of model ethanol acceptors thus provides a simple and effective “toolbox” to investigate glycosylation reaction mechanisms and report on the robustness of glycosylation protocols.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...