Experimental and numerical insights into the formation of zirconia nanoparticles: a population balance model for the nonaqueous synthesis†
Abstract
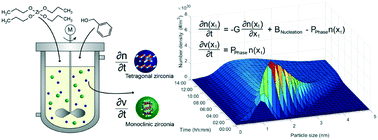
The nonaqueous synthesis of zirconia nanoparticles was investigated to elucidate the complex interplay between process parameters and final nanoparticle properties. We determined the chemical reaction kinetics and derived a model equation for the reaction constant to describe the course of the synthesis as a function of temperature and precursor concentration. While investigating the nucleation kinetics, we were able to show via small-angle X-ray scattering that particles nucleate in roundish shapes in a size regime of 2 nm. The current understanding of the tetragonal-to-monoclinic phase transformation was extended by a novel model that relates the probability of particles undergoing the phase transition to the particle size. The derived model functions result in a comprehensive population balance equation framework that can simulate the entire particle formation process to predict final nanoparticle properties as well as their evolvement during the synthesis. Supported by the simulation results, we unravel why monoclinic particles are present in the final product in smaller sizes than tetragonal particles which at first seems to be in conflict with thermodynamics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...