Facile synthesis of a dopant-free hole transporting material with a phenothiazine core for planar perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
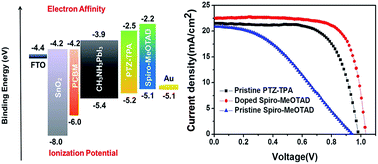
A novel electron-rich small-molecule, 4,4′-(10-(4-octylphenyl)-10H-phenothiazine-3,7-diyl)bis(N,N-(4-methoxyphenyl)anilene) (PTZ-TPA), containing phenothiazine as the core with triphenylamine side groups, was synthesized via a Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. When PTZ-TPA was incorporated into a CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cell as a dopant-free hole transporting material (HTM), a short circuit photocurrent density of 21.5 mA cm−2, an open circuit voltage of 0.982 V, and a fill factor of 0.679 were obtained, giving rise to an overall power conversion efficiency of 14.3%, which is comparable to the power conversion efficiency obtained using the current state-of-the-art HTM 2,20,7,70-tetrakis(N,N′-di-p-methoxyphenylamine)-9,90-spirobifluorene with dopant (Spiro-MeOTAD, power conversion efficiency of 17.1%). PTZ-TPA is thus a promising HTM with the potential to replace the expensive Spiro-MeOTAD owing to its comparable performance and much simpler synthesis route; it also presented a better stability during a one week aging test compared with Spiro-MeOTAD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...