Graphene based nanosensor for aqueous phase detection of nitroaromatics
Abstract
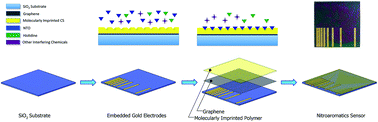
A graphene-based nanosensor was fabricated to selectively detect nitrotriazolone (NTO) molecules with a molecularly imprinted film via simple electrical measurements. Molecularly imprinted polymer comprising chitosan was used as sensitive layer. Gold electrodes for electrical measurements were lithographically fabricated on Si/SiO2 substrate, followed by monolayer graphene transfer and polymeric film coating. Monolayer graphene and molecularly imprinted polymer were characterized by ATR-FTIR, UV-Vis, SEM and Raman spectroscopy. Transfer-length measurements (TLM) indicate that the sensor selectively and linearly responds against aqueous NTO solutions within a wide range of concentration of 0.01–0.1 mg mL−1 that covers the lowest toxic level of NTO determined by USEPA. This nanosensor with embedded electrodes is re-usable and suitable for field applications, offering real-time electrical measurements unlike current techniques where complex analytics are required.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...