First-principles study on intrinsic defects of SnSe
Abstract
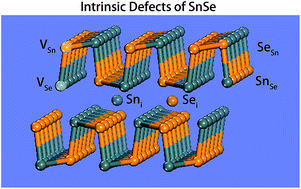
The formation energies and electronic properties of intrinsic defects of SnSe, including two vacancies (VSn and VSe), two interstitials (Sni and Sei) and two antisites (SnSe and SeSn), are investigated by using density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The results indicate that, due to a relatively low formation energy as well as a desirable ultra-shallow transition energy level, VSn can act as an effective source for p-type conduction under both Sn- and Se-rich conditions, which implies that SnSe is a native p-type semiconductor. On the other hand, a native n-type conduction is unlikely to be realized due to the absence of effective intrinsic sources. In addition, all the three types of intrinsic defects are not capable of inducing magnetism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...