Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial evaluation of nanofibrillated cellulose grafted by a novel quinolinium silane salt
Abstract
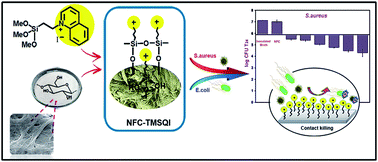
Nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) is a bio-based nanomaterial with no intrinsic antibacterial properties. In the present study, an NFC derivative with antibacterial properties was prepared by chemical grafting of a novel quinolinium silane salt containing a reactive trimethoxysilane group on the surface of its nanofibrillar network. First, (3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)quinolinium iodide (TMSQI) was synthesized using (3-chloropropyl trimethoxysilane) (CPTMS) and quinoline in the presence of potassium iodide. Then, the synthesized TMSQI was covalently grafted on the surface of NFC by a simple adsorption-curing process. The synthesized TMSQI was characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopies. The grafted NFC samples were also characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, elemental analysis, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and thermogravimetric analysis and also tested for antibacterial activity against Gram-positive (S. aureus) and Gram-negative (E. coli) bacteria. The TMSQI-grafted NFC exhibited a successful killing effect against Gram-positive bacteria, whereas bacteriostatic efficiency was found in the grafted NFC samples against Gram-negative bacteria.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors’ collection: Antimicrobial Polymers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...