Bovine serum albumin-loaded nano-selenium/ICG nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy†
Abstract
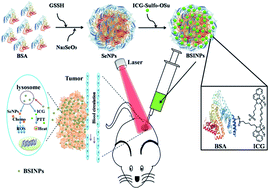
A combination of chemotherapy and photothermal treatment has already become a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Hence, it is highly desirable to develop a safe and effective delivery system. In the present study, we have developed bovine serum albumin-loaded nano-selenium (SeNPs)/indocyanine green (ICG) nanoparticles (BSINPs) that were generated by a programmed assembly method. They could simultaneously deliver SeNPs (a chemotherapeutic agent) and ICG (a photothermal agent) to tumor regions for combined chemo-photothermal therapy. BSINPs presented good monodispersity, a suitable size, fluorescence stability, and characteristic spectral features in comparison with free ICG. Moreover, the BSINPs displayed a longer retention time in tumors and a higher temperature response under laser irradiation. In addition, the process of subcellular location in vitro and the distribution of BSINPs in vivo could be monitored. The combined therapy offered by the BSINPs with laser irradiation synergistically induced the death of U87L glioma cells, and completely inhibited U87L tumor growth in vivo compared with chemo or photothermal therapy alone. Outstandingly, no tumor recurrence or treatment-induced toxicity was observed after a single-dose of BSINPs with laser irradiation. The results indicate that the well-defined BSINPs are highly desirable for cancer treatment with chemo-photothermal therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...