A peptide-decorated and curcumin-loaded mesoporous silica nanomedicine for effectively overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer cells†
Abstract
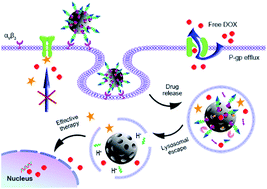
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is a major obstacle to the success of cancer chemotherapy, which is closely associated with the overexpression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and the endolysosomal capture of drug. Therefore, to explore a strategy that could down-regulate P-gp expression and promote drugs escaping from the endolysosome is highly desired for overcoming MDR in chemotherapeutic treatment. This work reports a peptide-functionalized mesoporous silica nanomedicine (MSN) for encapsulation of curcumin (CUR) and doxorubicin (DOX) to significantly reverse the MDR in consequence of rapid endolysosomal escape and the inhibition of P-gp function. The nanomedicine is modified with the peptide of GFLGHHHRRGDS to encapsulate CUR and DOX with high loading efficiency and content. It can be selectively uptaken by the DOX resistant MCF-7/ADR cells via the specific recognition between RGDS and αvβ3 integrin to enter into lysosomes. Afterwards, the GFLG is cleaved by the lysosomal cathepsin B to release CUR and DOX from MSN. Furthermore, the imidazole-rich HHHR peptide can induce effective lysosomal membrane permeability which is beneficial for drug escape from lysosome, CUR-mediated inhibition of P-gp, and nuclear import of DOX in MCF-7/ADR cells. Confocal fluorescence imaging, flow cytometry and MTT assays demonstrate that the combination of CUR and the peptide-functionalized MSN markedly enhances the intracellular DOX concentration and achieves a successful chemotherapeutic treatment to MCF-7 or MCF-7/ADR cells, thus this work offers an effective strategy to overcome MDR.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...