A wheat straw cellulose based semi-IPN hydrogel reactor for metal nanoparticles preparation and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol
Abstract
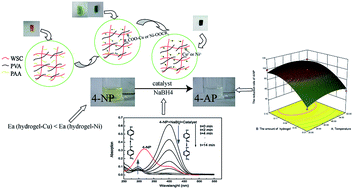
A wheat straw cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid)/poly(vinyl alcohol) semi-IPN hydrogel (WSC-g-PAA/PVA) was synthesized. Copper and nickel nanoparticles were prepared in situ inside the above hydrogel and then applied as a catalyst to reduce 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersion spectrum (EDS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and diffraction analysis (XRD) were employed to characterize the hydrogel–nanometal composite. The operation parameters on reduction of 4-NP were optimized by using the well-known response surface methodology (RSM) based on Box–Behnken design (BBD). Three experimental parameters including reaction temperature, the amount of hydrogel–M (metal) and the amount of NaBH4 on the 4-NP reduction were evaluated. The optimal values of the operation parameters under the related constraint conditions were obtained at 30 °C with 0.07 g of catalyst and 0.07 g of NaBH4 for hydrogel–Cu, and at 30 °C with 0.08 g of catalyst and 0.12 g of NaBH4 for hydrogel–Ni. It was found that the activation energies were 17.30 kJ mol−1 and 19.48 kJ mol−1 for hydrogel–Cu and hydrogel–Ni, respectively, by the analysis of thermodynamics of the reduction reaction. According to the 5 repetitive uses, hydrogel–Cu possessed 98% activity and hydrogel–Ni had 97% activity. And, after being stored for 30 days, both composites retained 70% activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...