Stability behaviour of antiretroviral drugs and their combinations. 6: evidence of formation of potentially toxic degradation products of zidovudine under hydrolytic and photolytic conditions†
Abstract
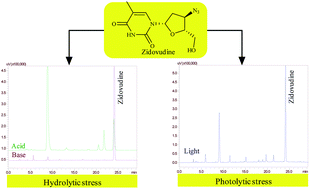
This study explored the comprehensive degradation behaviour of zidovudine (ZDV) under solution and solid stress conditions. In total, nine degradation products were detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The same were tentatively characterized with the help of high resolution and multistage mass spectrometry. Among them, five degradation products were also enriched and isolated with the help of semi-preparative HPLC and subjected to 1D and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance and/or infrared spectrometric studies to confirm their structures. The characterization of all the degradation products helped in outlining the comprehensive degradation pathway of ZDV. A significant finding was the formation of 3′-amino-3′-deoxythymidine (AMT) upon base hydrolysis as well as photolysis of the drug. This product is a known catabolite of the drug with a high degree of toxicity. Also, a few other degradation products formed during the study were predicted to have potential toxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...