Effect of erbium concentration on the structural, optical and electrical properties of a Bi4Ti3O12 system
Abstract
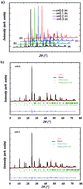
We have studied the influence of erbium doping on the optical and electrical properties of a Bi4Ti3O12 compound. Bi4−xErxTi3O12 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3) samples are prepared by the solid state reaction method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed that our samples are homogenous and crystallize in the orthorhombic system with the Fmmm space group. Absorbance measurement reveals that the peak intensity increases with increasing erbium concentrations and this behavior confirms the good homogeneity of the samples. DC-conductivity measurements show that all samples are characterized by a semiconductor behavior. It is found that electrical conductivity is reduced considerably with increasing erbium content up to x = 0.3. This is due to the decrease in oxygen vacancy density. For the free compound, dc-conductivity is characterized by the appearance of a saturation region at a specific temperature (Tsat = 480 K). For Er doped compounds, Tsat goes beyond 600 K. An AC-conductivity study shows that the conductivity is governed by the jump relaxation model (JRM) and conduction through grain boundaries. We found that the conductivity spectrum of the investigated materials obeys the Jonscher universal double power law. The deduced activation energy increases when increasing the erbium content from Ea = 467 meV for x = 0 to Ea = 670 meV for x = 0.3. Increasing the Er substitution reduces the frequency dispersion of the real part of the dielectric constant ε′. Also, the tan δ plot indicates that the investigated samples exhibit the characteristics of a relaxor dielectric.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...