Antibacterial and catalytic activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles prepared by using an aqueous extract of green coffee bean as a reducing agent
Abstract
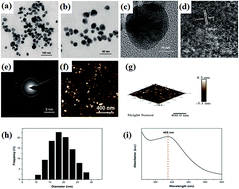
Spherical biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were synthesized using aqueous green coffee bean extract as a reducing agent. The green coffee bean extract was used for the time to reduce silver ions via a one-step, green, and rapid approach. The prepared AgNPs were characterized via transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and UV-visible spectroscopy. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) was performed to measure the particle size. These AgNPs exhibit strong antibacterial activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of AgNPs for Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus are 0.05 μmol L−1 and 0.1 μmol L−1, respectively. Furthermore, AgNPs could serve as an effective catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol in the presence of NaBH4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...