Effective optimization of surface passivation on porous silicon carbide using atomic layer deposited Al2O3
Abstract
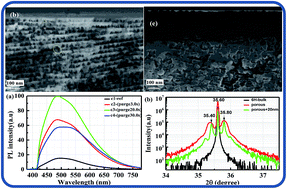
Porous silicon carbide (B–N co-doped SiC) produced by anodic oxidation showed strong photoluminescence (PL) at around 520 nm excited by a 375 nm laser. The porous SiC samples were passivated by atomic layer deposited (ALD) aluminum oxide (Al2O3) films, resulting in a significant enhancement of the PL intensity (up to 689%). The effect of thickness, annealing temperature, annealing duration and precursor purge time on the PL intensity of ALD Al2O3 films was investigated. In order to investigate the penetration depth and passivation effect in porous SiC, the samples were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-resolved PL. The optimized passivation conditions (20 nm Al2O3 deposited at 160 °C with purge time of 20 s, followed by an annealing for 5 min at 350 °C) for porous SiC were achieved and the results indicate that surface passivation by ALD Al2O3 thin films is a very effective method to enhance the luminescence efficiency of porous SiC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...