Phosphazene-based novel organo-inorganic hybrid salt: synthesis, characterization and performance evaluation as multifunctional additive in polyol
Abstract
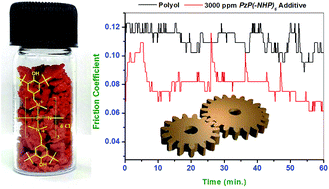
A novel organo-inorganic hybrid salt, namely, hexa-P-(N,N′-dimethylaminomethyl-3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)cyclotriphosphazene hexachloride [N3P3{–N(R1)2–CH2–C6H2(OH)R22}6]6Cl− (R1 = CH3, R2 = C(CH3)3), which was denoted as PzP(-NHP)6, was synthesized by the reaction between hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene (N3P3Cl6) and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol in dichloromethane. The synthesized salt was characterized using elemental analysis (CHN), UV-vis, infrared (IR), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and thermogravimetry (TG). The salt was then evaluated as a multifunctional antioxidant, anticorrosion, antiwear and antifriction additive in a polyol lube base oil. PzP(-NHP)6 was found to display excellent antioxidant and moderate anticorrosion properties as estimated by the RBOT (rotating bomb oxidation test) according to ASTM D2272 and standard corrosion test procedures, respectively. Four-ball tests according to ASTM D4172B were performed in order to evaluate its antiwear and antifriction characteristics in terms of the average wear scar diameter (AWSD) and average friction coefficient, respectively. It was found that PzP(-NHP)6 at a doping concentration of 3000 ppm reduced the AWSD of the blank polyol from 695.83 ± 16.86 to 585.83 ± 11.72 μm, whereas the average friction coefficient decreased from 0.110 ± 0.0077 to 0.080 ± 0.0097.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...