Influence of electronic structure on visible light photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped TiO2†
Abstract
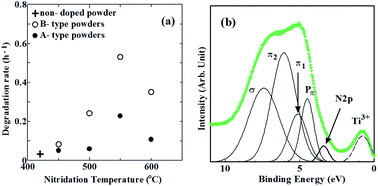
Nitrogen (N)-doped TiO2 thin films were synthesized by sol–gel methods from precursor solutions with or without urea and post calcination in NH3 gas. Their structural and electronic properties were characterized by X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy utilizing synchrotron radiation. N-doped TiO2 powders were synthesized for the estimation of visible light photocatalytic activities. N-doped TiO2 thin films revealed polycrystalline anatase phases. N was chiefly doped into substitutional sites. The densities of N and defects (oxygen vacancies and reduced Ti species) increased with elevating calcination temperature. Localized states associated with doped N were successfully found from shoulder structures of valence band spectra, which were located at 0.24 eV to 0.34 eV above the valence band maximum in the band gap. Incorporated N enhanced the photocatalytic activity, whereas defects reduced it. The highest photocatalytic activity was obtained by synthesizing N-doped TiO2 powders from a precursor solution with urea and subsequent calcination at 550 °C due to high-density N and low-density defects. Consequently, the optimum N/O atomic ratio was shown to be approximately 0.06. It became possible to achieve heavier N doping and better photocatalytic activity under vis light irradiation using urea than any other study only using NH3 gas for nitridation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...