Shape-controlled electrochemical synthesis of mesoporous Si/Fe nanocomposites with tailored ferromagnetic properties†
Abstract
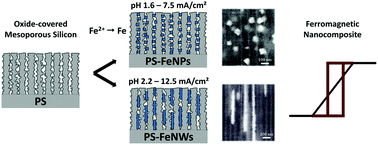
This study reports on an original and efficient way to synthesize iron nanowires and cubic-shaped nanoparticles by electrochemical deposition on a mesoporous silicon host and its impact on magnetic properties. The selective growth of iron nanostructures inside the pores can be achieved, thanks to the presence of a native oxide layer on the pore walls, suggesting a surface-state assisted electrochemical process. Because of hydrogen coevolution, the pH of the solution controls the shape of the iron nanostructures (particles or wires) while the electrodeposition current density can be adjusted to suppress the parasitic deposition on top of the structure. Under optimal conditions, nanowires with lengths up to 2 μm are synthesized after 15 seconds of deposition. Magnetic characterization of the ferromagnetic nanowire composite exhibits an easy axis of magnetization in the pore direction due to shape anisotropy with a remanence ratio of 0.6. The shape anisotropy of the nanoparticle composite is weaker than for the nanowire composite because of the homogeneous dispersion of the particles. The versatility of the mesoporous silicon framework is thus a considerable asset to tune the nanocomposite’s magnetic properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...