Glass surface modification via Cu(0)-mediated living radical polymerization of fluorinated and non-fluorinated acrylates
Abstract
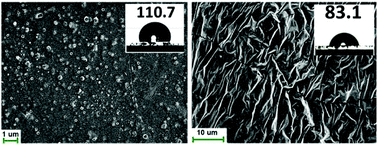
Terminal silanol groups on the glass surface were used for the chemical bonding of α-bromo amide as the initiator for surface initiated Cu(0)-mediated living radical polymerization (LRP) to graft well-defined poly(butyl arylate) (PBA) and poly(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl methacrylate) (PTFEM) brushes on the glass surface. A grafting to methodology was also performed by the modification of the glass surface using a thiosilane agent and performing a thio-bromo click reaction in the presence of PBA and PTFEM synthesized via Cu(0)-mediated LRP. Furthermore, a one-pot grafting to method was developed that proved a facile, fast, and efficient method for grafting a bromo-terminated polymer to the glass surface in one step. All glass slides were characterized using ATR-FTIR and UV-vis spectroscopy, water contact angle measurements and SEM. The surface topology and roughness of selected samples were analyzed using AFM. Results show that an ultrathin layer of a polymer with nanoscale features and high roughness was chemically grafted to the glass surface without compromising glass transparency. These methodologies can be used to graft well-defined polymers with different functionalities on the glass surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...