Ratiometric imaging of lysosomal hypochlorous acid enabled by FRET-based polymer dots†
Abstract
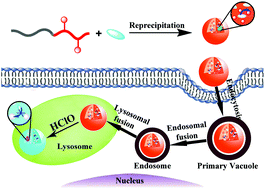
The development of an effective method for imaging of lysosomal hypochlorous acid (HClO) is of great significance to better understand the roles of HClO-related diseases. Herein, we report on the fabrication of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based fluorescent polymer dots (FPD) for the ratiometric imaging of lysosomal HClO in living cells via a simple co-precipitation method. This FRET-based construction strategy takes the advantage of flexible design by incorporating target-inert fluorogen (donor) and target-sensitive fluorogen (acceptor) into the nanoparticle to avoid leakage and photobleaching problems. The as-prepared FPD exhibits good water dispersibility, fast response (<30 s), high sensitivity (∼5.1 nM), outstanding selectivity, excellent photostability and long-term stability (>15 weeks). Moreover, the resultant FPD with good membrane permeability could mainly locate in the lysosomes and act as a probe for the ratiometric imaging of lysosomal HClO in living HeLa cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...