New copper(i) complex based initiating systems in redox polymerization and comparison with the amine/benzoyl peroxide reference†
Abstract
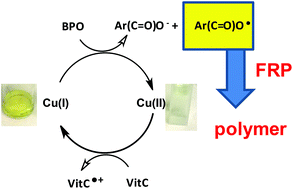
Novel copper complex based initiating systems for redox free radical polymerization (FRP) of methacrylate resins under mild conditions are proposed. Remarkably, the FRP performance of the Cu(I)/ascorbic acid (Vitamin C – VitC)/benzoyl peroxide (BPO) redox system is noticeably more significant than that of the amine/BPO reference especially at the top surface where the oxygen inhibition is particularly deleterious. The Cu(I)/BPO interaction leads to a decomposition of the peroxide and generates a benzoyl radical and Cu(II) as a byproduct. The ascorbic acid acts as a reducing agent and allows the regeneration of Cu(I) from Cu(II). Hydroperoxides formed at the surface through the radical/O2 interaction are also decomposed by the new proposed Cu complex leading to additional polymerization initiating species. The structure/reactivity relationship of the new proposed Cu(I) complexes in the Cu(I)/VitC/BPO systems is studied. The use of Cu(I)/VitC/BPO/iodonium salt systems in redox photoactivated FRP is also explored.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...