Self-assembly of poly(ionic liquid) (PIL)-based amphiphilic homopolymers into vesicles and supramolecular structures with dyes and silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
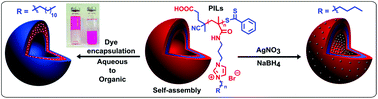
The incorporation of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments in homopolymers leads to their self-assembly into nanostructures in selective solvents, owing to their amphiphilic character. Here we report the RAFT polymerization of N-imidazole-3-propylmethacrylamide and the further quaternization of the resulting polymer with different alkyl bromides of a varying chain length, which afforded well-defined polymeric ionic liquids (PILs) 1–4. These PILs are characterized by the presence of both hydrophobic alkyl chains and hydrophilic ionic moieties, allowing their spontaneous self-assembly in water, forming distinct polymeric vesicles (= polymersomes) the size of which can be varied as a function of alkyl chain length. As demonstrated by the dye-encapsulation study, a particular organic-soluble PIL, 3, consisting of a dodecyl side-chain enabled the transfer of the water-soluble Rose Bengal dye, from an aqueous solution to the organic phase. In addition, polymersomes obtained from a PIL (2) featuring butyl side chains were used as templates and polymeric stabilizers of silver nanoparticles (NPs), i.e. leading to AgNP@PIL hybrids, as observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). It was found that the extent of functionalization of polymersomes by the Ag-based NPs varied greatly before and after the end-group removal of the PIL. Altogether, this report emphasizes the facile synthesis of amphiphilic homoPILs and their manipulation in water for dye encapsulation and for stabilization of silver NPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...