A dendrimer–hydrophobic interaction synergy improves the stability of polyion complex micelles†
Abstract
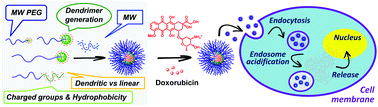
Polyion complex (PIC) micelles incorporating PEG-dendritic copolymers display an unprecedented stability towards ionic strength that is amplified via hydrophobic interactions. The tridimensional orientation of peripheral hydrophobic linkers between charged groups and the globular/rigid dendritic scaffold maximizes this stabilization compared to PIC micelles from linear polymers. As a result, micelles stable at concentrations higher than 3 M NaCl are obtained, which represents the highest saline concentration attained with PIC micelles. Advantages of this stabilizing dendritic effect have been taken for the design of a robust, pH-sensitive micelle for the controlled intracellular release of the anticancer drug doxorubicin. This micelle displays a slightly higher toxicity, and distinctive mechanisms of cell uptake and intracellular trafficking relative to the free drug. The preparation of mixed PIC micelles by combining differently functionalized PEG-dendritic block copolymers has allowed the fine-tuning of their stability, paving the way towards the facile modulation of properties like biodegradability, drug loading, or the response to external stimuli.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...