A chiral interpenetrating polymer network constructed by helical substituted polyacetylenes and used for glucose adsorption†
Abstract
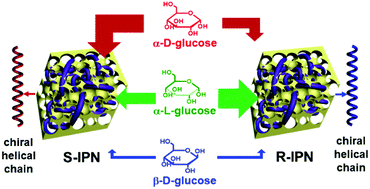
Incorporating multi-functions into a single entity can provide various novel materials, well exemplified by interpenetrating polymer networks. In this contribution, we prepared the first chiral porous interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) by incorporating functional boronic acid-containing polymers to a pre-formed chiral porous framework which was constructed by chirally helical substituted polyacetylenes. The pore size in the resulting chiral IPNs can be tuned by adjusting the content of the boronic acid-containing polymer. Circular dichroism and UV-vis absorption spectra demonstrated that the helical polymer chains in both the pre-formed chiral porous framework and the final IPNs took preferential helicity, which rendered the IPNs with considerable optical activity. The as-prepared IPNs could adsorb glucose through esterification reaction occurring between the boronic acid groups contained in the networks and cis-diol in glucose. More importantly, the successful combination of boronic acid groups with the chiral framework enabled the IPNs to simultaneously exhibit enantioselectivity and pH sensitivity in the glucose adsorption process. The reversibility of the boronic acid-derived ester structure facilitated the IPNs to be easily recycled, thus endowing the novel IPNs with diverse promising applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...