Microporous polyimide networks constructed through a two-step polymerization approach, and their carbon dioxide adsorption performance†
Abstract
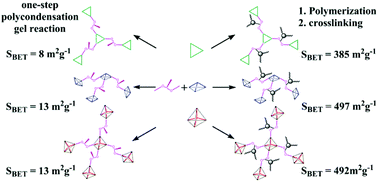
Based on a dianhydride monomer 2,5-bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenoxy)-4′-phenylethynyl biphenyl (PEPHQDA) containing a crosslinkable phenylethynyl pendant group, microporous polyimide networks (HBPI-CRs) were prepared through a two-step pathway combining polymerization and crosslinking reactions. Specifically microporous features such as surface morphology, microporous structure and uniform nanometer-sized pore channels were introduced to the polyimide networks through this two-step pathway. The HBPI-CR networks exhibited a BET surface area (385–497 m2 g−1) as well as a comparable CO2 uptake (1.65–2.04 mmol g−1 at 273 K and 1 bar) and enthalpy of adsorption (28.6–30.0 kJ mol−1) to that of other microporous polyimides derived from rigid tri-dimensional monomers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...