Photochemical and computational studies of inclusion complexes between β-cyclodextrin and 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinones†
Abstract
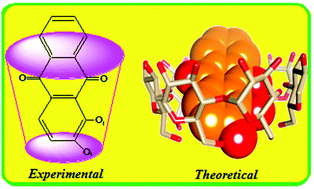
The formation of an inclusion complex between 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinones (1,2-DHAQ) and β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) has been studied by UV-visible, fluorescence spectroscopy and electrochemical methods. The stoichiometric ratio of the inclusion complex was found to be 1 : 1 and the binding constant was evaluated using the Benesi–Hildebrand equation. The peak currents (Ipa and Ipc) change drastically with increasing β-CD concentration and the peak potentials (Epa and Epc) shifted. A mechanism is proposed to explain the inclusion process. A stable solid inclusion complex was prepared using a co-precipitation method and it is characterized by FT-IR, XRD, DSC, SEM, and 1H NMR that confirmed the formation of the inclusion complex. The β-CD and 1,2-DHAQ inclusion complex obtained by molecular docking studies is in good correlation with the results obtained through experimental methods using PatchDock and FireDock servers. The virtual study of the energetically favorable complex was carried out by PM3 calculations and molecular orbital energy studies suggest that orientation A is more favourable than orientation B.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...