Low cost UVA-LED as a radiation source for the photo-Fenton process: a new approach for micropollutant removal from urban wastewater
Abstract
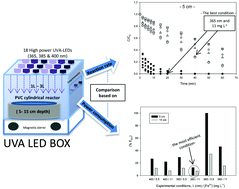
Light Emitting Diode (LED) technology has matured sufficiently to be considered as an alternative UVA radiation source in photoreactors. Currently, low energy consuming LEDs with a wide range of wavelengths and radiant flux are readily available. In this study, UVA-LEDs were used as a radiation source for the photo-Fenton process as tertiary treatment. The water matrix used was a simulated secondary effluent doped with 200 μg L−1 of the pesticide acetamiprid (ACTM) due to its recalcitrant nature. All experiments were carried out in a LED-box reactor at pH 2.8. The main purpose of this research was to gain some insight into the relationships among energy supply, LED consumption, UVA irradiance and reaction rate. The effect of LED wavelength on energy efficiency for ACTM degradation was studied by varying the iron concentration and liquid depth. Three wavelengths (365, 385 and 400 nm) and two iron concentrations (5 and 11 mg L−1) for two different liquid depths (5 and 15 cm) were evaluated in order to obtain more energy efficient conditions. The results suggest that while the wavelength of 365 nm with 11 mg Fe2+ L−1 was the best condition for ACTM degradation, the wavelength of 385 nm had slower kinetics, but higher energy efficiency.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solar chemistry & photocatalysis – environmental applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...