Isolation and identification of l/d-lactate-conjugated bufadienolides from toad eggs revealing lactate racemization in amphibians†
Abstract
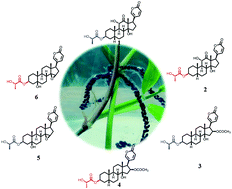
Three pairs of bufadienolide L/D-lactate epimers (1–6) were isolated from the eggs of the toad Bufo bufo gargarizans. The structures were elucidated by using spectroscopic methods, X-ray diffraction analysis and a modified Mosher's method. Compounds 1–6 represent the first occurrence of lactate-conjugated bufadienolides in nature, and illustrate the existence of an enzyme-controlled epimerization from L- to D-lactate in amphibians. The biosynthetic pathways, in which two key enzymes might be involved (i.e., lactate racemase and acyltransferase), were proposed. In addition, the biological assays revealed that compounds 1–4 are potent cytotoxic agents against human gastric cancer cells BGC-823 and human lung cancer cells A549 with IC50 values in a range of 8.0 to 80.0 nM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...