Palladium-catalyzed highly regioselective hydroaminocarbonylation of aromatic alkenes to branched amides†
Abstract
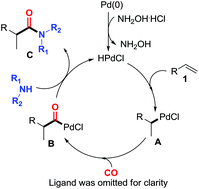
Pd(t-Bu3P)2 has been successfully identified as an efficient catalyst for the hydroaminocarbonylation of aromatic alkenes to branched amides under relatively mild reaction conditions. With hydroxylamine hydrochloride as an additive, both aliphatic and aromatic amines could be used as coupling partners for the present reaction, leading to production of branched amides in high yields with excellent regioselectivities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...