Bacterial self-defense antibiotics release from organic–inorganic hybrid multilayer films for long-term anti-adhesion and biofilm inhibition properties
Abstract
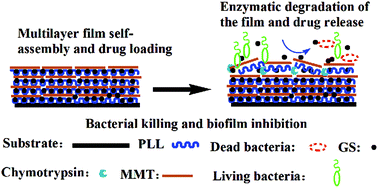
Implant-associated bacterial infections pose serious medical and financial issues due to the colonization and proliferation of pathogens on the surface of the implant. The as-prepared traditional antibacterial surfaces can neither resist bacterial adhesion nor inhibit the development of biofilm over the long term. Herein, novel (montmorillonite/poly-L-lysine-gentamicin sulfate)8 ((MMT/PLL-GS)8) organic–inorganic hybrid multilayer films were developed to combine enzymatic degradation PLL for on-demand self-defense antibiotics release. Small molecule GS was loaded into the multilayer films during self-assembly and the multilayer films showed pH-dependent and linear growth behavior. The chymotrypsin- (CMS) and bacterial infections-responsive film degradation led to the peeling of the films and GS release. Enzyme-responsive GS release exhibited CMS concentration dependence as measured by the size of the inhibition zone and SEM images. Notably, the obtained antibacterial films showed highly efficient bactericidal activity which killed more than 99.9% of S. aureus in 12 h. Even after 3 d of incubation in S. aureus, E. coli or S. epidermidis solutions, the multilayer films exhibited inhibition zones of more than 1.5 mm in size. Both in vitro and in vivo antibacterial tests indicated good cell compatibility, and anti-inflammatory, and long-term bacterial anti-adhesion and biofilm inhibition properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...