The dendritic effect and magnetic permeability in dendron coated nickel and manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles†
Abstract
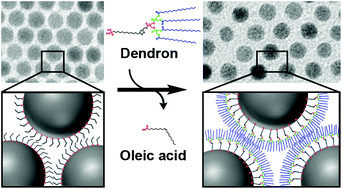
The collective magnetic properties of nanoparticle (NP) solid films are greatly affected by inter-particle dipole–dipole interactions and therefore the proximity of the neighboring particles. In this study, a series of dendritic ligands (generations 0 to 3, G0–G3) have been designed and used to cover the surface of magnetic NPs to control the spacings between the NP components in single lattices. The dendrons of different generations introduced here were based on the 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic acid (Bis-MPA) scaffold and equipped with an appropriate surface binding group at one end and several fatty acid segments at the other extremity. The surface of the NPs was then modified by partial ligand exchange between the primary stabilizing surfactants and the new dendritic wedges. It was shown that this strategy permitted very precise tuning of inter-particle spacings in the range of 2.9–5.0 nm. As expected, the increase in the inter-particle spacings reduced the dipole–dipole interactions between magnetic NPs and therefore allowed changes in their magnetic permeability. The dendron size and inter-particle distance dependence was studied to reveal the dendritic effect and identify the optimal geometry and generation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...