Site-specific conjugation of an antibody on a gold nanoparticle surface for one-step diagnosis of prostate specific antigen with dynamic light scattering†
Abstract
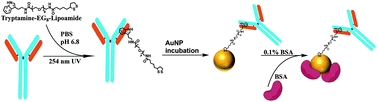
Small dimensions of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) necessitate antibodies to be immobilized in an oriented fashion in order to conserve their antigen binding activity for proper function. In this study, we used the previously described UV-NBS method to site-specifically incorporate a thioctic acid (TA) functionality into antibodies at the conserved nucleotide-binding site (NBS). Modified antibodies were immobilized on the AuNP surface in an oriented manner utilizing the newly incorporated TA functionality while maintaining the antibody structure and activity. The resulting antibody functionalized AuNPs via the UV-NBS method demonstrated significantly enhanced antigen detection capabilities and improved antigen detection sensitivity with a high level of selectivity when compared to other commonly used AuNP functionalization methods. Our results demonstrate that the limit of detection (LOD) for AuNPs functionalized via the UV-NBS method was 55 pM PSA, which is 40, 851, and 5873-fold improved over the other immobilization methods: EDC-NHS, thiol reduction, and ionic interaction, respectively. Consequently, the UV-NBS method provides a universal, site-specific functionalization method that generates highly sensitive and more stable antibody functionalized AuNPs which are amenable to any available detection and treatment assay with potential significant implications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...