Advanced carbon dots via plasma-induced surface functionalization for fluorescent and bio-medical applications†
Abstract
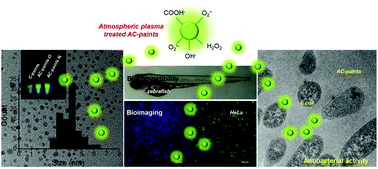
Multifunctional carbon-based nanodots (C-dots) are synthesized using atmospheric plasma treatments involving reactive gases (oxygen and nitrogen). Surface design was achieved through one-step plasma treatment of C-dots (AC-paints) from polyethylene glycol used as a precursor. These AC-paints show high fluorescence, low cytotoxicity and excellent cellular imaging capability. They exhibit bright fluorescence with a quantum yield twice of traditional C-dots. The cytotoxicity of AC-paints was tested on BEAS2B, THLE2, A549 and hep3B cell lines. The in vivo experiments further demonstrated the biocompatibility of AC-paints using zebrafish as a model, and imaging tests demonstrated that the AC-paints can be used as bio-labels (at a concentration of <5 mg mL−1). Particularly, the oxygen plasma-treated AC-paints (AC-paints-O) show antibacterial effects due to increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in AC-paints (at a concentration of >1 mg mL−1). AC-paints can effectively inhibit the growth of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii). Such remarkable performance of the AC-paints has important applications in the biomedical field and environmental systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...