Layer-dependent electronic properties of phosphorene-like materials and phosphorene-based van der Waals heterostructures†
Abstract
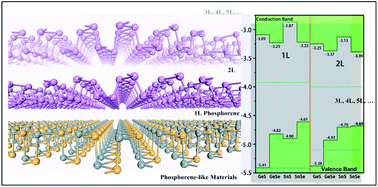
Black phosphorus is a layered semiconducting allotrope of phosphorus with high carrier mobility. Its monolayer form, phosphorene, is an extremely fashionable two-dimensional material which has promising potential in transistors, optoelectronics and electronics. However, phosphorene-like analogues, especially phosphorene-based heterostructures and their layer-controlled electronic properties, are rarely systematically investigated. In this paper, the layer-dependent structural and electronic properties of phosphorene-like materials, i.e., mono- and few-layer MXs (M = Sn, Ge; X = S, Se), are first studied via first-principles calculations, and then the band edge position of these MXs as well as mono- and few-layer phosphorene are aligned. It is revealed that van der Waals heterostructures with a Moiré superstructure formed by mutual coupling among MXs and among MXs and few-layer phosphorene are able to show type-I or type-II characteristics and a I–II or II–I transition can be induced by adjusting the number of layers. Our work is expected to yield a new family of phosphorene-based semiconductor heterostructures with tunable electronic properties through altering the number of layers of the composite.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editor’s Choice: van der Waals heterostructures


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...