Perturbation of the pulmonary surfactant monolayer by single-walled carbon nanotubes: a molecular dynamics study†
Abstract
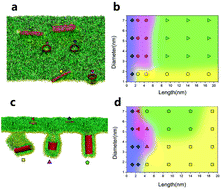
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are at present synthesized on a large scale with a variety of applications. The increasing likelihood of exposure to SWCNTs, however, puts human health at a high risk. As the front line of the innate host defense system, the pulmonary surfactant monolayer (PSM) at the air–water interface of the lungs interacts with the inhaled SWCNTs, which in turn inevitably perturb the ultrastructure of the PSM and affect its biophysical functions. Here, using molecular dynamics simulations, we demonstrate how the diameter and length of SWCNTs critically regulate their interactions with the PSM. Compared to their diameters, the inhalation toxicity of SWCNTs was found to be largely affected by their lengths. Short SWCNTs with lengths comparable to the monolayer thickness are found to vertically insert into the PSM with no indication of translocation, possibly leading to accumulation of SWCNTs in the PSM with prolonged retention and increased inflammation potentials. The perturbation also comes from the forming water pores across the PSM. Longer SWCNTs are found to horizontally insert into the PSM during inspiration, and they can be wrapped by the PSM during deep expiration via a tube diameter-dependent self-rotation. The potential toxicity of longer SWCNTs comes from severe lipid depletion and the PSM-rigidifying effect. Our findings could help reveal the inhalation toxicity of SWCNTs, and pave the way for the safe use of SWCNTs as vehicles for pulmonary drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...