Transformation from single-mesoporous to dual-mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles†
Abstract
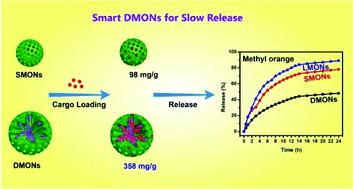
Transformation from single-mesoporous to dual-mesoporous structured organosilica nanoparticles can be achieved by simply varying the volume fraction of ethanol in the synthesis system, using lauryl sulfonate betaine and sodium dodecyl sulfonate as dual-templates. Core–shell structured dual-mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles possess smaller mesopores (4.0 nm) in the shell and flower-like larger mesopores (46 nm) in the core. Owing to the unique mesostructure, dual-mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles show a high loading capacity and a slow release rate for cargo molecules. The large mesopores on the inside can provide a large storage space for the guest molecules and the small mesopores in the outer shell act as a natural valve, slowing the release. In addition, both single-mesoporous and dual-mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles, exhibit low cell toxicity and excellent cell permeability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...