Assessing the relative stability of copper oxide clusters as active sites of a CuMOR zeolite for methane to methanol conversion: size matters?†
Abstract
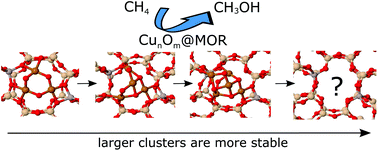
Copper-containing zeolites exhibit high activity in the direct partial oxidation of methane into methanol at relatively low temperatures. Di- and tricopper species have been proposed as active catalytic sites, with recent experimental evidence also suggesting the possibility of the formation of larger copper oxide species. Using density functional theory based global geometry optimization, we were able to identify a general trend of the copper oxide cluster stability increasing with size. For instance, the identified ground-state structures of tetra- and pentamer copper clusters of CunOn2+ and CunOn−12+ stoichiometries embedded in an 8-ring channel of mordenite exhibit higher relative stability compared to smaller clusters. Moreover, the aluminium content and localization in the zeolite pore influence the cluster's stability and its geometrical motif, which offers a perspective of tuning the properties of copper-exchanged zeolites by creating copper oxide clusters of a given structure and size. With the activity of the cluster towards methane being connected to its stability, such tuning will potentially allow the design of catalysts with engineered properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...