Nanoporous microstructures mediate osteogenesis by modulating the osteo-immune response of macrophages†
Abstract
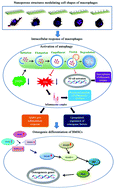
The osteoimmune environment plays indispensable roles in bone regeneration because the early immune environment that exists during the regenerative process promotes the recruitment and differentiation of osteoblastic lineage cells. The response of immune cells growing on nanotopographic surfaces and the microenvironment they generate should be considered when evaluating nanotopography-mediated osteogenesis, which are topics that are generally neglected in the field. In this study, we investigated the modulatory effects of nanoporous anodic alumina with different sized pores on macrophage responses and their subsequent effects on the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). The nanopore structure and the pore size were found to be important adhesive cues for macrophages, which affected their spreading and cell shape, subsequently regulated the expression and activation of autophagy pathway components (LC3A/B, Beclin-1, Atg3, Atg7, and P62) and modulated the inflammatory response, osteoclastic activities, and release of osteogenic factors. Subsequently, the osteogenic pathways (Wnt and BMP) of BMSCs were found to be regulated by different nanopore-induced inflammatory environments, which affected the osteogenic differentiation outcomes. This study is the first to emphasize the effects of immune cells on nanotopography-mediated osteogenesis, which could lead to a new strategy for the development of advanced nanobiomaterials for tissue engineering, nanomedicine and immunotherapeutic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...