Efficient coverage of ZnO nanoparticles on cotton fibres for antibacterial finishing using a rapid and low cost in situ synthesis†
Abstract
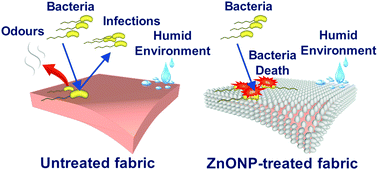
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) have received considerable attention as an antibacterial agent particularly in the textile industry. In the present work a successful procedure for in situ growth of ZnONPs in textiles was developed. The results obtained showed that a combination of in situ synthesis and the sol–gel method promoted a uniform and dense adsorption of the nanoparticles both inside and on the surface of fabric fibres. The fabrics finished with ZnONPs have been investigated for antibacterial properties by the agar diffusion method and by the absorption method according to the ISO 20743:2013 standard and exhibited an antibacterial effect against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus ATCC33591, Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC1228, Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 and Propionibacterium acnes ATCC6919. Moreover, tests conducted with hydrogen peroxide suggested the involvement of reactive oxygen species, namely the involvement of hydrogen peroxide, in the antibacterial activity of the zinc oxide nanoparticles. Therefore, the synthesised nanoparticles showed great potential to be used as coatings for medical, cosmetic or sports fabrics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...