Voltammetric determination of trace amounts of permanganate at a zeolite modified carbon paste electrode†
Abstract
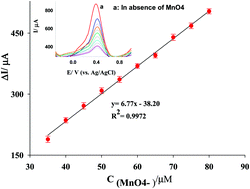
A novel sensitive, simple and fast method is suggested for indirect voltammetric determination of permanganate in aqueous solution. The method is based on the modification of a carbon paste electrode (CPE) by Fe(II)-exchanged clinoptilolite nanoparticles (Fe(II)-NClin). When permanganate was added to H2SO4 supporting electrolyte, the voltammetric peak current of the Fe(II)/Fe(III) redox system was decreased. Hence, this decrease in the peak current was used for indirect determination of permanganate. The results of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) confirmed that the modified Fe(II)-NClin/CPE electrode has a remarkable charge transfer ability with respect to the raw CPE and NClin/CPE electrodes. The interaction effects of more influencing variables in square wave voltammetry were studied by an experimental design method using response surface methodology (RSM). The optimal run was obtained as: pH 2.0, amplitude = 0.5 V, modifier% = 16.5 and step potential = 0.023 V. Under the optimum conditions, the square wave voltammetric current of the Fe(II)-NClin/CPE was inversely proportional to permanganate in the concentration range from 35 to 80 nmol L−1 with a detection limit of 0.40 nmol L−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...