Investigation of cobalt(iii)–TPA complexes as potential bioreductively activated carriers for naphthoquinone-based drugs†
Abstract
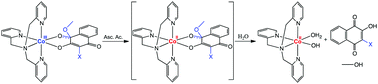
Four cobalt(III)–TPA complexes with 2-hydroxy-3-X-1,4-naphthoquinones (HNQ-X), X = methyl (1), chlorine (2), bromine (3) and iodine (4), were designed and investigated as potential bioreductively activated carriers for naphthoquinone-based drugs. The substituents X were used in order to avoid dimerization of the naphthoquinone ligands and evaluate their effect on the Co3+/Co2+ potential. The expected [Co(TPA)(NQ-X)]2+ species was obtained for the NQ-CH3 ligand in 1, while the chlorine, bromine and iodine derivatives fostered the attachment of a methoxide to the C(1)carbonyl atom to produce complexes 2, 3 and 4, respectively. The structure and electronic properties of the complexes were investigated by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis and DFT calculations. Cyclic voltammetry analysis showed that the Co3+/Co2+ potential is 0.21 V for complex 1 and 0.32 V vs. SHE for complexes 2–4. Redox activation with dissociation of the naphthoquinones was successfully achieved by reduction of the complexes with the biologically relevant reducing agent ascorbic acid.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...