A simple and low-cost route to recycle rare earth elements (La, Ce) from aqueous solution using magnetic nanoparticles of CoxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0.2 and 0.8): synthesis, isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption
Abstract
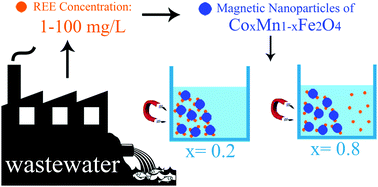
The use of rare earth elements has increasingly grown in recent years because of their special chemical, electrical, optical and metallurgical properties. In this work, a low-cost, highly efficient and stable magnetic nano-adsorbent is proposed to recycle rare earth cations (La and Ce) from aqueous solution. Magnetic nanoparticles of CoxMn1−xFe2O4 with x = 0.2 and 0.8 were synthesized by a simple co-precipitation method and employed in a La3+ and Ce3+ adsorption process. To characterize the adsorbent and compare the effects of different x values, XRD, FE-SEM, EDS, VSM, BET and DLS were employed. Furthermore, the adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics were studied. To understand the nature of the reactions, the Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) model was applied to the experimental data. Desorption properties were also investigated to evaluate adsorbent reusability. All the results confirmed that the magnetic nanoparticles of CoxMn1−xFe2O4 (especially x = 0.2) have considerable potential as an efficient, low-cost, stable and reusable adsorbent for recycling La and Ce cations from aqueous solutions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...