Synthesis of a dibenzo-BODIPY-incorporating phenothiazine dye as a panchromatic sensitizer for dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
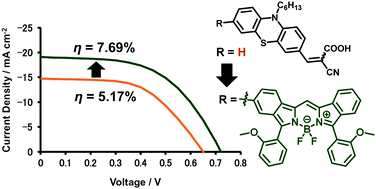
For the application of metal-free organic sensitizers in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), a boron dibenzopyrromethene (dibenzo-BODIPY)-conjugated phenothiazine dye with cyanoacrylic acid as an anchoring group 1 was synthesized and characterized. It showed an intense absorption band at 638 nm as the λmax value and a molar extinction coefficient (ε) of 1.23 × 105 M−1 cm−1. In addition, a relatively small but significant peak was observed at 440 nm (ε = 1.80 × 104 M−1 cm−1). Such panchromatic features allowed the fabrication of a DSSC with an excellent short-circuit current density (Jsc) of 19.09 mA cm−2 under 100 mW cm−2 AM1.5G simulated light. The corresponding external quantum efficiency (EQE) indicated that the cell converted the light to a photocurrent in a wide wavelength region up to 780 nm, resulting in a power conversion efficiency (PCE; η) of 7.69% in an I−/I3− redox couple electrolyte without the addition of any coadsorbents. When compared to the control cell loaded with a cycanoacrylic acid-appended phenothiazine 2, the PCE value of the 1-loaded cell was 1.5 times larger than that of the control cell because of significant enhancements in both Jsc and open-circuit voltage (Voc). Electrochemical impedance analysis (EIS) suggested attenuation of the charge recombination when using 1 as a sensitizer. In this way, the 1-loaded cell showed relatively good DSSC properties comparable to those of the cell with N719 (η = 7.15%) under the same conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...