A rhodamine based fluorescent trivalent sensor (Fe3+, Al3+, Cr3+) with potential applications for live cell imaging and combinational logic circuits and memory devices†
Abstract
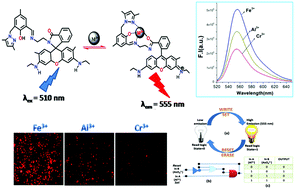
A sensor (HL5) based on rhodamine 6G–en and 3-(3,5-dimethyl-pyrazol-1-ylmethyl)-2-hydroxy-5-methyl-benzaldehyde (HL4) has been developed for a highly sensitive and selective CHEF based recognition of trivalent metal ions M3+ (M = Al, Fe and Cr) over mono- and di-valent and other biologically abundant trivalent metal ions with prominent enhancement in absorption and emission intensities. A large enhancement of fluorescence intensities for Fe3+ (21 fold), Al3+ (14 fold) and Cr3+ (10 fold) was observed upon addition of 1.8 equivalents of these metals into the probe in methanol/H2O (1 : 1, v/v, pH 7.2) with the possibility of naked eye detection. The corresponding Kf values were evaluated to be 6.7 × 104 M−1 (Fe3+); 8.2 × 104 M−1 (Al3+) and 6.0 × 104 M−1 (Cr3+). The quantum yields of HL5 and [HL5–Fe3+] and [HL5–Cr3+] and [HL5–Al3+] complexes in methanol/H2O (1 : 1, v/v, pH 7.2) are found to be 0.013, 0.290, 0.120, and 0.158, respectively, using rhodamine-6G as the standard. The LOD for Fe3+, Al3+ and Cr3+ were determined by 3σ methods with values 0.29, 0.34 and 0.31 μM, respectively. An arsenate ion snatches Al from the Al–HL5 complex and quenches its fluorescence via its ring closed spirolactam form. Advanced level molecular logic devices using the inputs 2 and 4 and memory devices, have been constructed. The low cytotoxicity and large enhancement in fluorescence intensity of HL5 upon complexation with M3+ metal ions make the probe suitable for bio-imaging of M3+ (M = Al, Fe and Cr) in living cells and native cellular iron pools.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...