A novel cationic iridium(iii) complex with a thiorhodamine-based auxiliary ligand: application for luminescent and colorimetric detection of Hg2+ in an aqueous solution†
Abstract
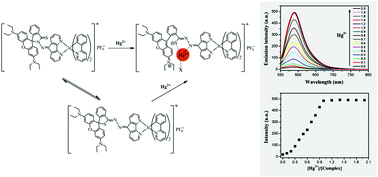
A novel cationic iridium(III) complex [(SRB-DAF)Ir(ppy)2]PF6 (SRB-DAF: 2-((5H-cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,4-b′]dipyridin-5-ylidene)amino)-3′,6′-bis(diethylamino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthene]-3-thione and ppy: 2-phenylpyridine) with a thiorhodamine-based auxiliary ligand was designed and synthesized. The spirolactam ring of the thiorhodamine group will be opened with the chelation of Hg2+ ion, and the iridium(III) complex instantly exhibits remarkable “turn-on” type naked-eye detectable color (λmax,abs = 567 nm) and phosphorescence (λmax,em = 587 nm) changes. Hg2+ can be detected by this iridium(III) complex with high selectivity and sensitivity in an aqueous solution in the presence of other metal cations (Ag+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Ni2+, Ba2+, Cr3+, Ca2+, Co2+, Na+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Li+, Mn2+, Al3+, K+ and Cd2+) in the pH range 6.9–8.0. As a Hg2+ probe, the iridium(III) complex exhibited low detection limits of 8.074 × 10−8 M (16 ppb) by luminescence detection and 3.985 × 10−7 M (80 ppb) by absorption detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...